Many tall tales have been told about calcium boluses but, our science isn’t fiction.
It’s true. Data supporting the superior efficacy of YMCP Vitall® is legendary. Read on for the rest of the story.
September 8, 2025
It’s true. Data supporting the superior efficacy of YMCP Vitall® is legendary. Read on for the rest of the story.
Calcium-only boluses for cows have long been marketed as beneficial, but research shows these calcium bolus supplements fall short. Studies demonstrate that calcium-only boluses show no improvement in milk production, immune response, or inflammation control — highlighting why a multi-nutrient solution like YMCP Vitall® delivers superior results
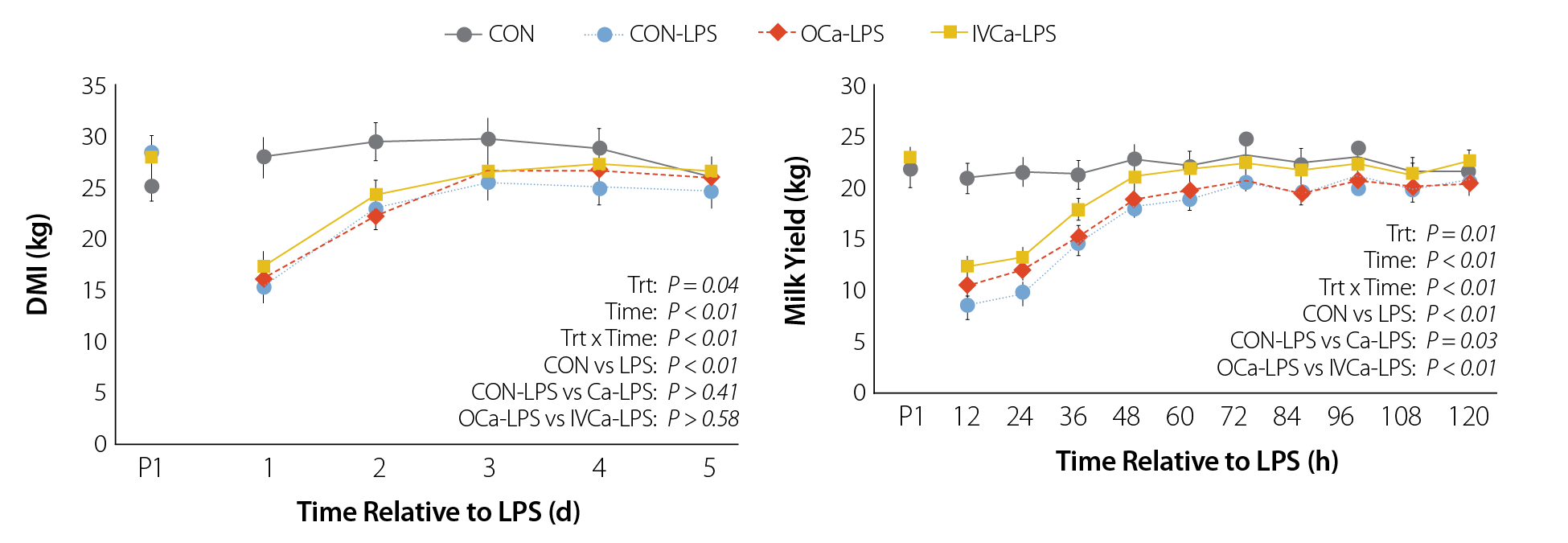
Don’t believe the fairy tales, believe the data. Results from a recent LPS challenge trial with calcium-only boluses showed:
• NO improvement in milk production
• NO improvement in mitigating inflammation
• NO improvement in immune response
Opegenorth, J., et al., J. Dairy Sci., 108 (2024), pp. 2883-2896
Yes, YMCP Vitall contains calcium but also live yeast to help get fresh cows eating. Along with magnesium, potassium and niacin, YMCP Vitall helps meet nutrient requirements for lactation, provides robust immune support and helps mitigate inflammation. The result is a happier outcome for cows.
| Nutrients | Role in Immunity | Reference |
| Magnesium |
Magnesium is involved in around 300 enzyme reactions. Free magnesium ions influence the potential at the cell membranes and act as a second messenger in the immune system. |
Bovine Immunology: Implications for Dairy Cattle. Vlasova, A. N., Saif, L. J., Front. Immunol., 12(2021):643206 |
| Calcium |
Intracellular calcium signaling is a key early feature in immune cell activation. |
Parturition and hypocalcemia blunts calcium signals in immune cells of dairy cattle. Kimura, K., Reinhardt, T.A., Goff, J.P., J. Dairy Sci. 89(2006):2588-95 |
| Potassium |
Impacts carbohydrate metabolism, amino acid uptake and protein synthesis, which aid in milk production as well as reproductive performance, immune function and cow well-being. |
Effect of dietary calcium and stage of lactation on potassium balance in lactating Holstein cows through 20 weeks of lactation. Jarrett, J.P., Taylor, M.S., Nennich, T.D., Knowlton, K.F., Harrison, J., Block, E., Prof. Animal Sci., 28(2012):502-506 |
| Niacin |
Alleviates the inflammatory response. |
Niacin Alleviates Dairy Cow Mastitis by Regulating the GPR109A/AMPK/NRF2 Signaling Pathway. Wenjin, G., et al, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21(2020): 3321 |
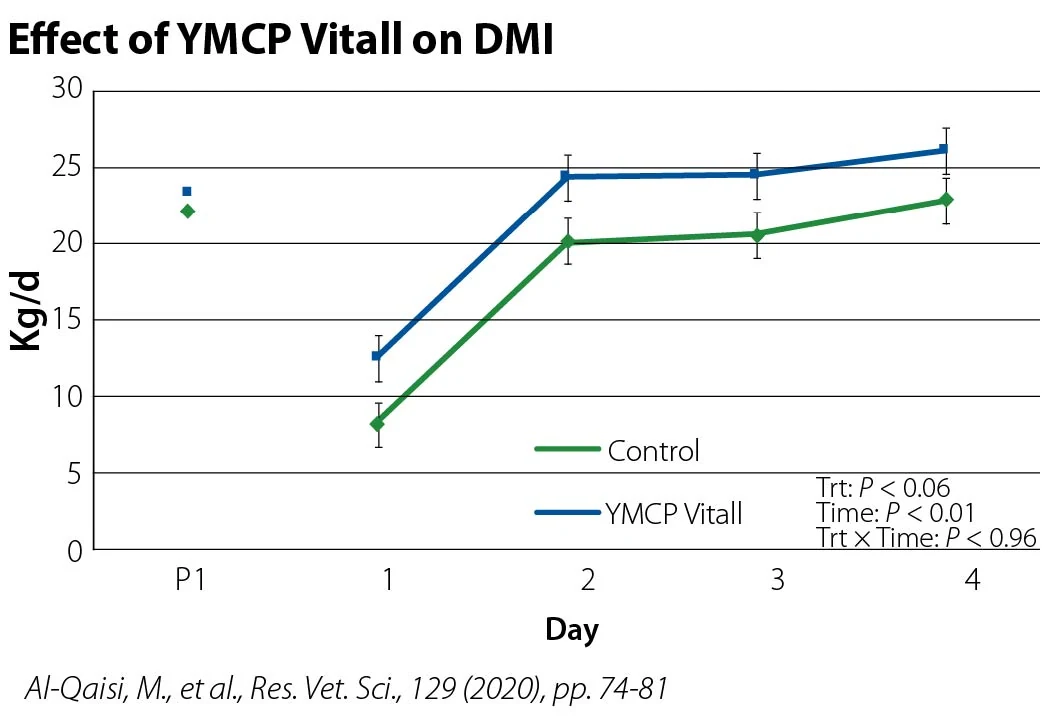
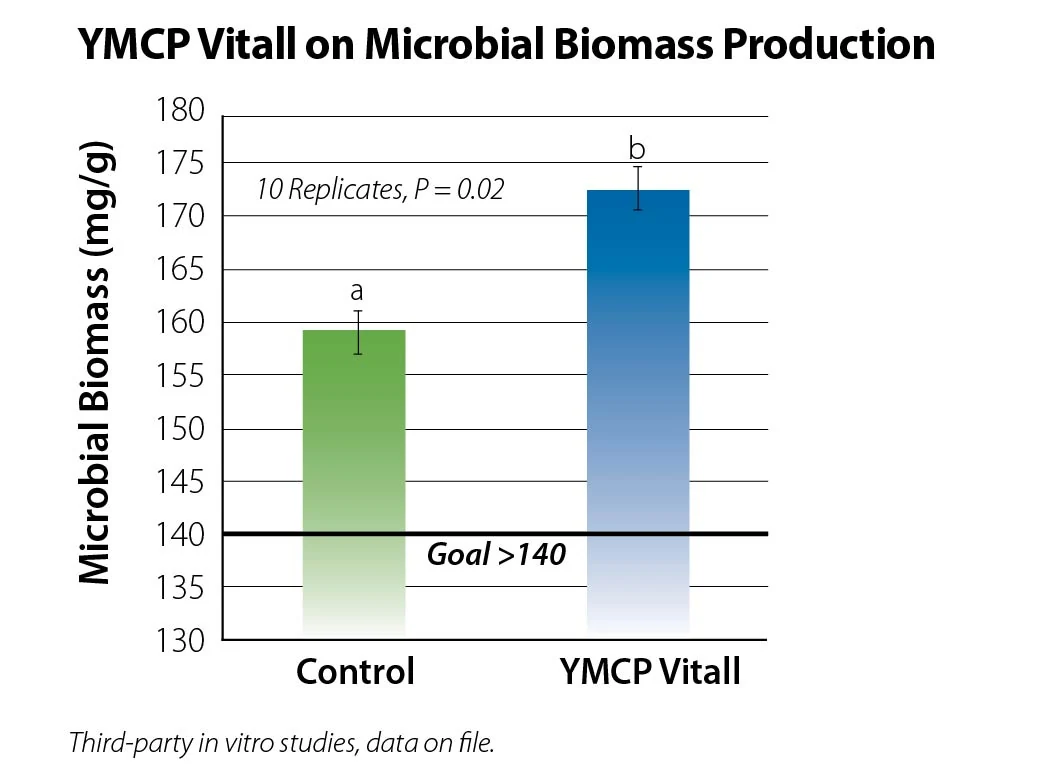
Dietary changes to higher starch lactation diets can result in rumen acidosis and can depress dry matter intake (DMI). YMCP Vitall encourages feed intake by helping the microbiome adapt to the new ration following DMI depression and promotes overall enteric health.
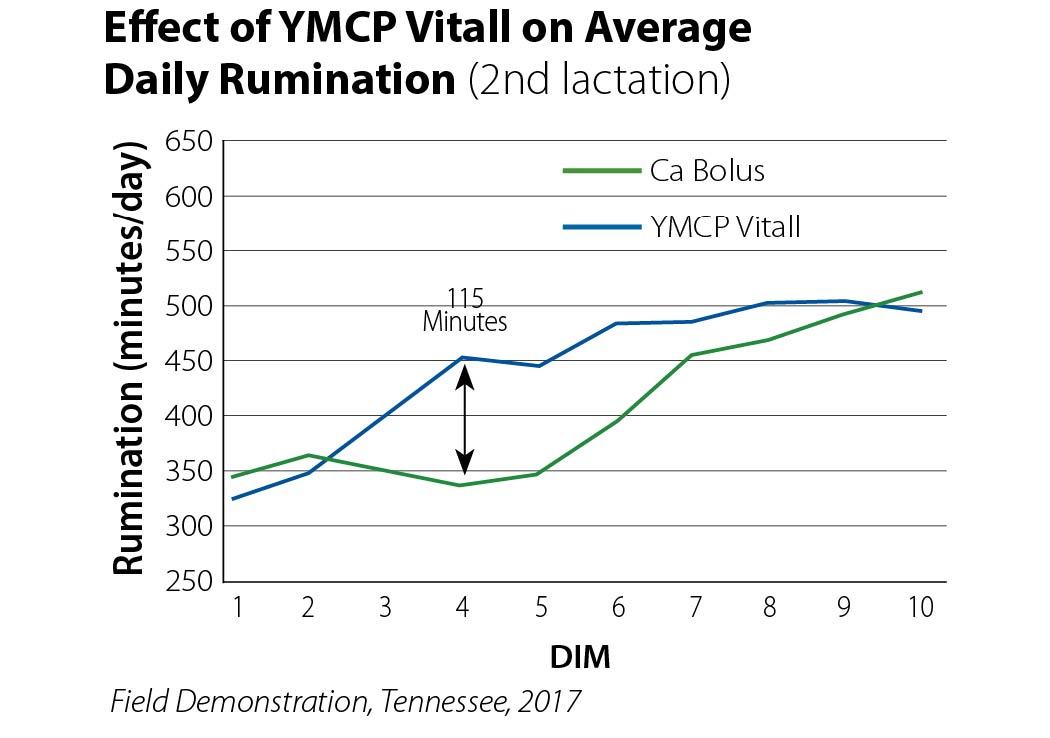
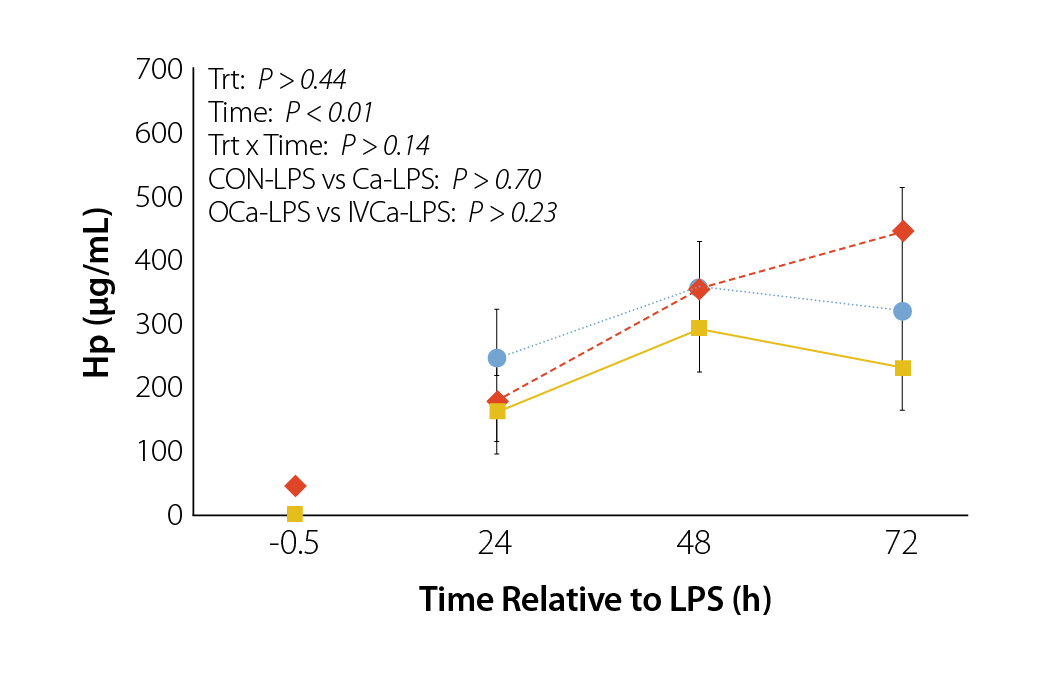
This university study explored a feed restricted diet followed by a high starch diet.
Results:
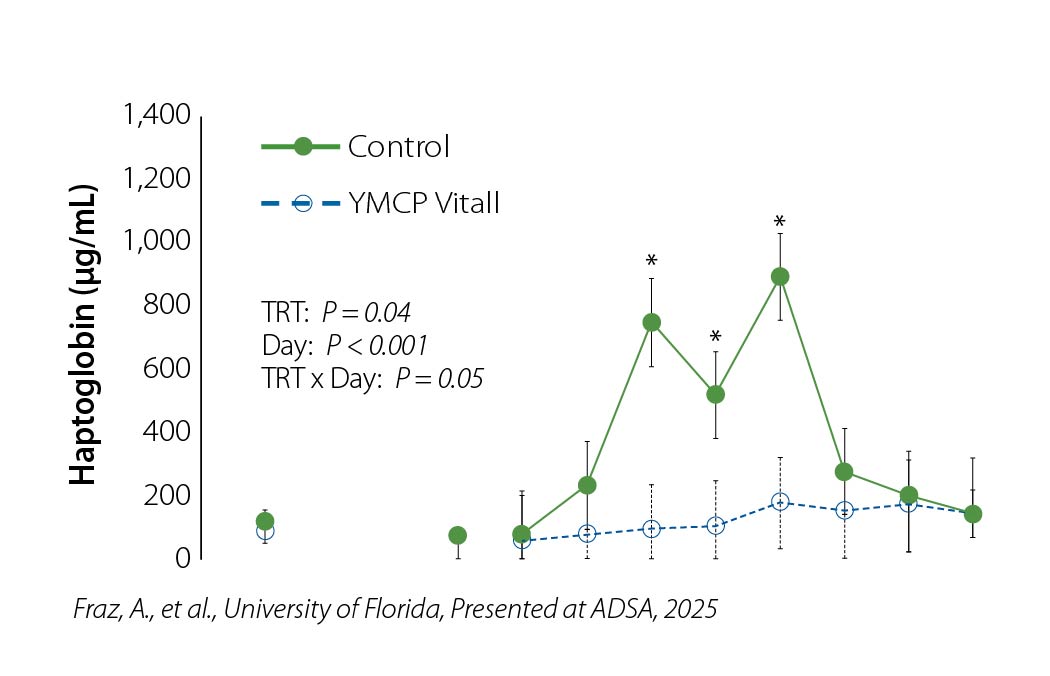
• Haptoglobin increased in Control, indicating greater degree of inflammation
• YMCP Vitall attenuated Inflammation, indicated by decrease haptoglobin
• YMCP Vitall improved blood Ca status
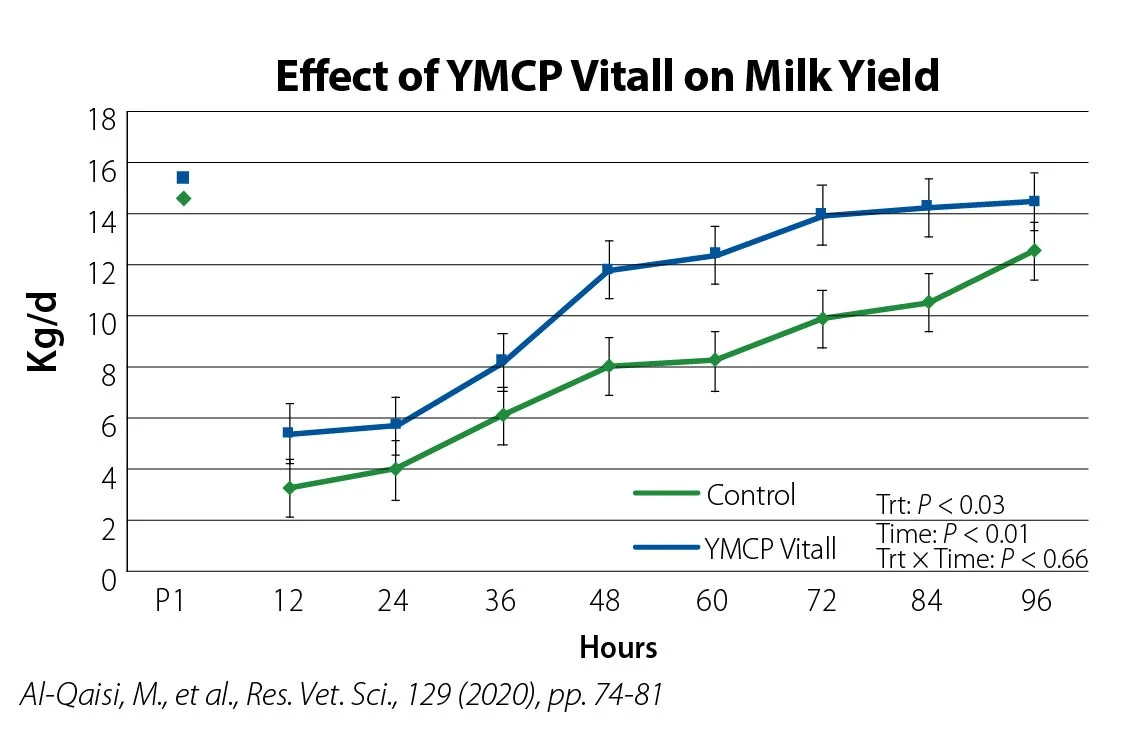
YMCP Vitall encourages feed intake, helping prepare fresh cows for the new diet, new environment and new routine. Years of data show cows supplemented with YMCP Vitall have consistently improved production despite the variety of geographic regions, feed protocols, management practices and a cow’s lactation status.
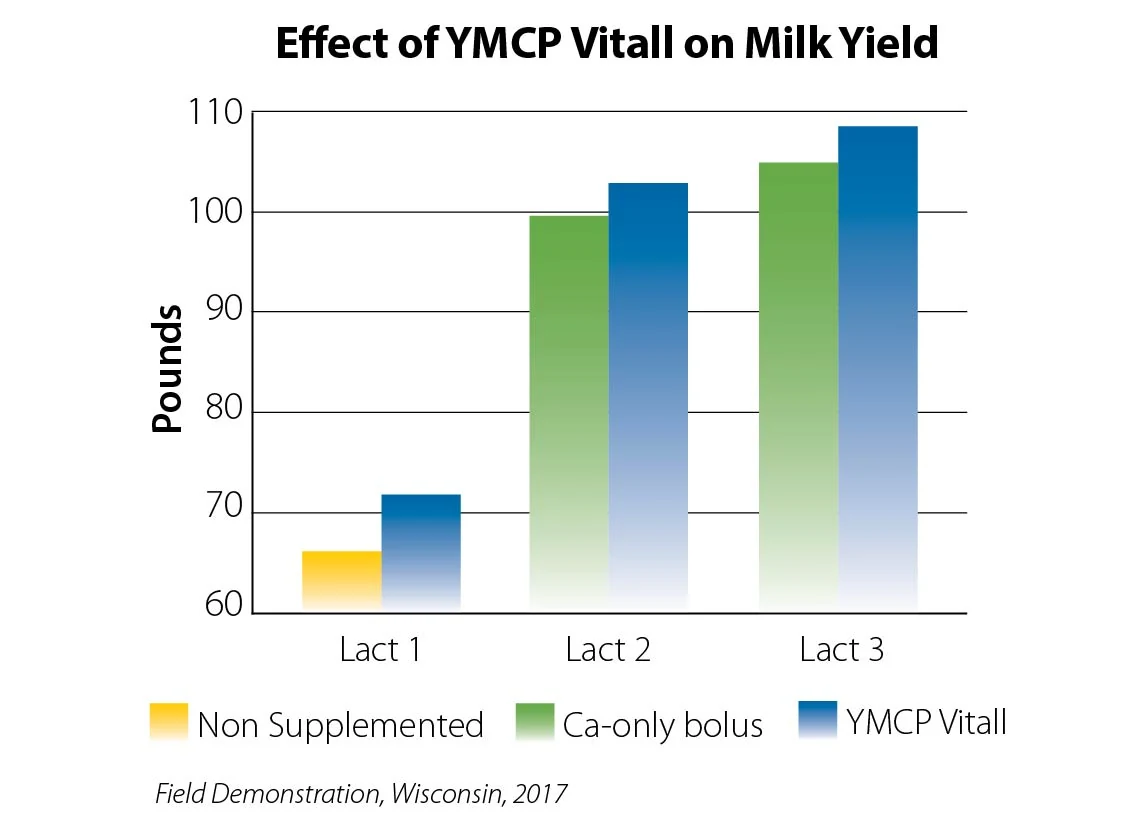
Physiologically, a fresh cow needs more than a calcium bolus. YMCP Vitall delivers calcium plus the essential nutrients to support recovery and performance. The data puts an end to the tall tales of calcium-only boluses.
Effects of maintaining eucalcemia following immunoactivation in lactating Holstein dairy cows.
Effects of an oral supplement containing calcium and live yeast on post-absorptive metabolism, inflammation and production following intravenous lipopolysaccharide infusion in dairy cows.
Evaluating the effects of an oral bolus containing live yeast and Ca, Mg, and K on the severity of a high-starch diet challenge.
Optimizing transition health and milk performance in Holstein dairy cows through an innovative oral effervescent bolus supplement with live yeast, minerals and antioxidants.
Effects of a yeast, mineral, and antioxidant bolus on transition cow performance under Flemish field conditions.
Effects of YMCP Vitall supplementation on rumination time post freshening in a commercial dairy in Tennessee.
Effects of YMCP Vitall supplementation in a Jersey commercial dairy in Tennessee.
Effects of YMCP Vitall supplementation in a Holstein commercial dairy in Israel.
Effects of YMCP Vitall supplementation on fresh cow health.
Comparing oral versus intravenous calcium administration on alleviating markers of production, metabolism, and inflammation during an intravenous lipopolysaccharide challenge in mid-lactation dairy cows.
Effects of oral calcium supplementation on productive and reproductive performance in Holstein cows.
Effects of inflammatory conditions on liver activity in puerperium period and consequences for performance in dairy cows.
A randomized clinical trial evaluating the effect of an oral calcium bolus supplementation strategy in postpartum Jersey cows on mastitis, culling, milk production, and reproductive performance.
Effect of oral calcium bolus supplementation on early-lactation health and milk yield in commercial dairy herds.
Modification of the feeding behavior of dairy cows through live yeast supplementation.
Effect of subclinical and clinical hypocalcemia and dietary cation-anion difference on rumination activity in periparturient dairy cows.
Differential effects of a single dose of oral calcium based on postpartum plasma calcium concentration in Holstein cows.
Field trial of 2 calcium supplements on early lactation health and production in multiparous Holstein cows.